Sage 100 Multi-Currency Series: What is FASB 52 and How does DSD Multi-Currency address it?
March 21, 2022

As mentioned in my blog, What types of Sage 100 users have DSD Multi-Currency?, one of the features in the suite of DSD Multi-Currency modules is FASB 52 Reporting compliance. Before we dive into how DSD Multi-Currency accomplishes this, let’s first define what FASB 52 Reporting entails.
What is FASB 52?
For US corporations that have foreign subsidiary companies, the financial reporting for the subsidiary company must be reported two ways: (1) Financial reporting in functional currency (also referred to as base currency of local currency) to the local government, and (2) Financial reporting in translated US Dollars to the US government.
For more detail information on the actual FASB reference, select this link from the FASB website: https://www.fasb.org/summary/stsum52.shtml
Modern ERP/Accounting software systems can easily accomplish the first reporting need. It’s the second one that is trickier. In order to be compliant in this reporting, you must report some General Ledger Account data translated to US Dollars using the current exchange rate while other data is translated and reported in US Dollars at historical exchange rates.
What does this mean, exactly? Here are a few examples:
- For accounts translated at the Current Exchange Rate: Take the Bank Account balance of CAD 10,000 (Canadian Dollars, which is the base currency) and multiply it by the today’s exchange rate (0.78537205 for example) to get the US translated amount of $7,853.48. This is the amount you would report for that General Ledger Account.
- For accounts translated at the Historical Exchange Rate: Take one detailed General Ledger posting for the account and multiply it by the exchange rate for the date of that transaction, then repeat for every detailed transaction for that account in the reporting period (various dates = various exchange rates) and then report the sum total of those translated postings.
As you can see, it’s the accounts translated at the Historical Exchange Rate that prove to be more difficult to report. There is a FASB 52 exception that allows you to report these historical-valued accounts using an average monthly exchange rate, but luckily DSD’s Multi-Currency stores the FASB 52 historical rates for every General Ledger transaction, so you do not have to resort to using an average rate.
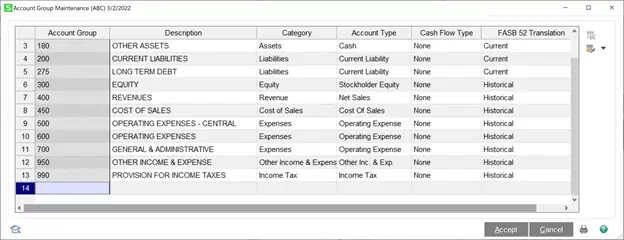
As far as which G/L Accounts use Current vs. Historical rates, P&L Accounts and Equity accounts use Historical valuation, while Assets & Liabilities use Current valuation. Note that there may be exceptions to certain accounts. Below is a sample account structure, with the FASB 52 Translation setting in the last column:
How does DSD Multi-Currency address FASB 52 Translation and Reporting?
First off, you would need the CUMC Multi-Currency Base Module and the GLMC General Ledger Multi-Currency enhancements installed to do FASB 52 Reporting. The CUMC Base Module allows for a user to define the FASB52 Currency (usually US Dollars) and associated daily exchange rates. The GLMC General Ledger Multi-Currency allows for the following:
- Assignment of FASB52 Translation method (Historical vs. Current) by Account Group, Main Account, and Account Number levels.
- Tracks the FASB 52 Exchange Rate (by date) and the translated Debit/Credit for every General Ledger Transaction, which is used for reporting Historical-translated accounts.
- Assignment of a FASB 52 Equity Adjustment Account, which balances out the Balance Sheet due Assets & Liabilities being valued at Current exchange rate, while Equity (P&L) is valued at Historical exchange rates.
- The Financial Reports, Trial Balance, G/L Detail Report and G/L Detail by Summary Report allow for printing in Base Currency or FASB 52 Currency. When printed in FASB 52 Currency, the report will automatically translate each account using the Current vs. Historical method.
- A Company Consolidation may also be performed to combine a Parent Company (US Dollars) with a Foreign Subsidiary Company (Base Currency = foreign currency, FASB 52 Currency = US Dollars) for consolidated reporting. This consolidation process will automatically perform the FASB 52 translation on the Foreign Subsidiary Company, resulting in a combined entity in US Dollars.
For more information on the step-by-step setup of FASB 52 in DSD Multi-Currency, stay on the look out for my next blog: Your guide to setting up FASB 52 in DSD Multi-Currency.
DSD Business Systems has been a Sage Development Partner, commonly referred to as a “Master Developer”, for the past 30 years. DSD currently has over 400 Enhancements to Sage 100 ERP and has created thousands of custom solutions for end-users around the world. We have had the privilege of working with hundreds of Sage consultants, resellers, and end-users to produce powerful custom solutions that enhance the functionality of Sage 100 ERP.
DSD Multi-Currency Q2 Promotion
New Multi-Currency Promotion Through June 30th, 2022!

Take advantage of our Multi-Currency promotion going on NOW through June 30th, 2022! Buy 3 or more Multi-Currency enhancements and get 1 free OR buy 5 or more Multi-Currency enhancements and get 2 free.